This determination is made on the basis of the facts and circumstances in each case and takes into account the nature of your business in its entirety. For example, if you lease only one passenger automobile during a tax year, you are not regularly engaged in the business of leasing automobiles. An employer who allows an employee to use the employer’s property for personal purposes and charges the employee for the use is not regularly engaged in the business of leasing the property used by the employee.
What are the factors that impact the book value of an asset?
The useful life of a patent or copyright is the lesser of the life granted to it by the government or the remaining life when you acquire it. However, if the patent or copyright becomes valueless before the end of its useful life, you can deduct in that year any of its remaining cost or other basis. Generally, if you can depreciate intangible property, you usually use the straight line method of depreciation. However, you can choose to depreciate certain intangible property under the income forecast method (discussed later). You must treat an improvement made after 1986 to property you placed in service before 1987 as separate depreciable property. Therefore, you can depreciate that improvement as separate property under MACRS if it is the type of property that otherwise qualifies for MACRS depreciation.

Declining Depreciation vs. the Double-Declining Method
- In the step chart above, we can see the huge step from the first point to the second point because depreciation expense in the first year is high.
- If you are not allowed to make the correction on an amended return, you may be able to change your accounting method to claim the correct amount of depreciation.
- Because you did not place any property in service in the last 3 months of your tax year, you used the half-year convention.
- As under reducing balance method assets are depreciated at a faster rate in the early stage of their useful life, it is a more suitable method for assets that have greater utility in the earlier years.
- If you use leased listed property other than a passenger automobile for business/investment use, you must include an amount in your income in the first year your qualified business-use percentage is 50% or less.
If you dispose of GAA property in a qualifying disposition, you can choose to remove the property from the GAA. A qualifying disposition is one that does not involve all the property, or the last item of property, remaining in a GAA and that is described by any of the following. For more information and special rules, see the Instructions for Form 4562. The SL method provides an equal deduction, so you switch to the SL method and deduct the $115. Basis adjustment due to recapture of clean-fuel vehicle deduction or credit.
Accounting Ratios
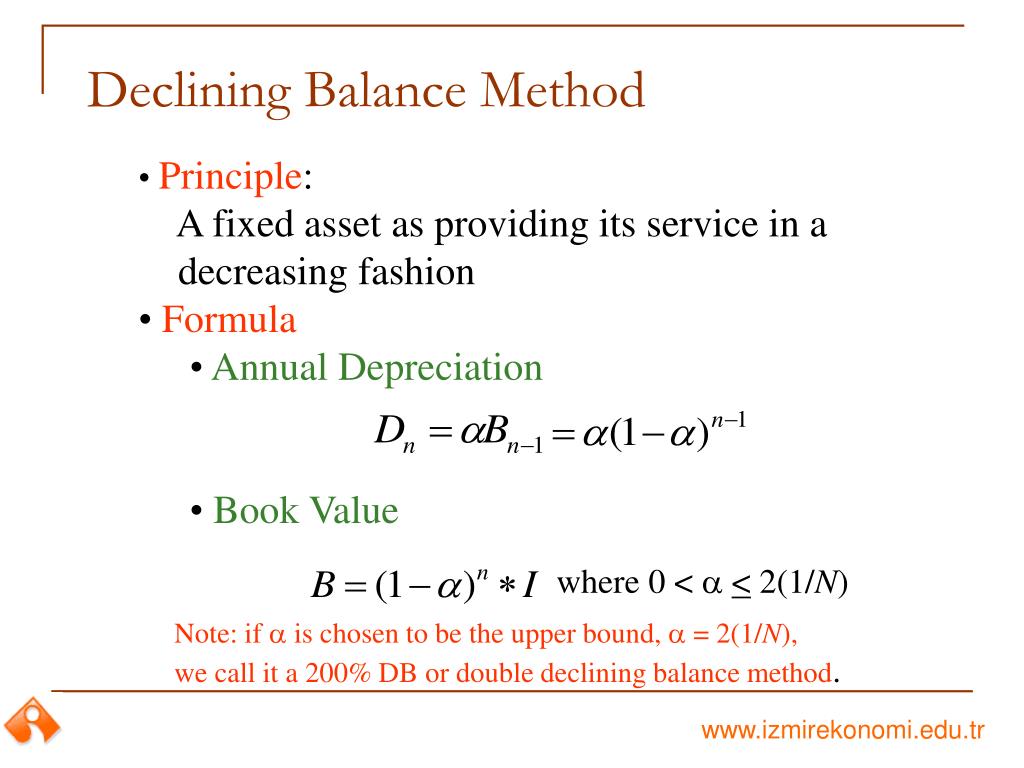
Where DBD is the declining-balance depreciation expense for the period, A is the accelerator, C is the cost and AD is the accumulated depreciation. Thus, the Machinery will depreciate over the useful life of 10 years at the rate of depreciation (20% in this case). As we can observe, the DBM results in higher depreciation during the initial years of an asset’s life and keeps reducing as the asset gets older. Reducing Balance Method is appropriate where an asset has a higher utility in the earlier years of its life.
Declining balance method of depreciation is an accelerated depreciation method in which the depreciation expense declines with age of the fixed asset. Depreciation expense under the declining balance is calculated by applying the depreciation rate to the book value of the asset at the start of the period. A declining balance method is used to accelerate the recognition of depreciation expense for assets during the earlier portions of their useful lives. This leaves less depreciation expense to be recognized later in their useful lives. To calculate depreciation under a declining method, multiply the book value of an asset at the beginning of the fiscal year by a multiple of the straight-line rate of depreciation. Examples of declining balance methods are the 150% declining balance method and the double declining balance method.
If you are in the business of renting videocassettes, you can depreciate only those videocassettes bought for rental. If the videocassette has a useful life of 1 year or less, you can currently deduct the cost as a business expense. Instead of including these amounts in the adjusted basis of the property, you can deduct the costs in the tax year that they are paid. You must also increase the 15-year safe harbor amortization period to a 25-year period for certain intangibles related to benefits arising from the provision, production, or improvement of real property. For this purpose, real property includes property that will remain attached to the real property for an indefinite period of time, such as roads, bridges, tunnels, pavements, and pollution control facilities.
Larry uses the inclusion amount worksheet to figure the amount that must be included in income for 2023. Larry’s inclusion amount is $224, which is the sum of −$238 (Amount A) and $462 (Amount B). For a description of related persons, see Related persons in the discussion on property owned or used in 1986 under What Method Can You Use To Depreciate Your Property? For this purpose, however, treat as related persons only the relationships listed in items (1) through (10) of that discussion and substitute “50%” for “10%” each place it appears. Treat the leasing of any aircraft by a 5% owner or related person, or the compensatory use of any aircraft, as a qualified business use if at least 25% of the total use of the aircraft during the year is for a qualified business use.
If you trade property, your unadjusted basis in the property received is the cash paid plus the adjusted basis of the property traded minus these adjustments. The recovery periods for most property are generally longer under ADS than they are under GDS. what is bank reconciliation Under GDS, property is depreciated over one of the following recovery periods. However, if this dual-use property does represent a significant portion of your leasing property, you must prove that this property is qualified rent-to-own property.
You can include participations and residuals in the adjusted basis of the property for purposes of computing your depreciation deduction under the income forecast method. The participations and residuals must relate to income to be derived from the property before the end of the 10th tax year after the property is placed in service. For this purpose, participations and residuals are defined as costs, which by contract vary with the amount of income earned in connection with the property. Because the double-declining balance method results in larger depreciation expenses near the beginning of an asset’s life—and smaller depreciation expenses later on—it makes sense to use this method with assets that lose value quickly. For example, if the fixed asset management policy sets that only long-term asset that has value more than or equal to $500 should be recorded as a fixed asset.
Under the declining balance methods, the asset’s salvage value is used as the minimum book value; the total lifetime depreciation is thus the same as under the other methods. As an alternative to systematic allocation schemes, several declining balance methods for calculating depreciation expenses have been developed. The declining balance technique represents the opposite of the straight-line depreciation method which is more suitable for assets whose book value drops at a steady rate throughout their useful lives. The rate of depreciation is defined according to the estimated pattern of an asset’s use over its useful life. The expense would be $270 in the first year, $189 in the second year, and $132 in the third year if an asset costing $1,000 with a salvage value of $100 and a 10-year life depreciates at 30% each year. Here’s the depreciation schedule for calculating the double-declining depreciation expense and the asset’s net book value for each accounting period.